Mortgage Rates: How to Get the Best Deal

What Are Mortgage Rates?
When buying a house, you may come across the words ‘mortgage rate’ and ‘term’. These words refer to the interest you will have to pay over the life of the mortgage loan. Many homebuyers do not know how the mortgage rate can affect their financial life. It is important to learn about these rates and the steps you need to take to get the best rates.

Definition of Mortgage Rates
Mortgage rate or mortgage interest rate is what costs you to borrow money to finance your home. The interest, instead of being paid as a lump sum, is paid as part of the monthly payment that you make on the principal amount of your loan.
What Is the Mortgage Interest Rate?
A mortgage rate is the interest rate that you pay on the amount of money that you have not yet repaid to the lender. There are two main types of mortgages. The first is the fixed-rate mortgage that has the interest rate staying the same. The second is the adjustable rate, where the interest rate keeps changing over time. As you continue to repay the principal amount in your loan, the interest amount keeps decreasing. The increasingly greater part of your payment goes toward building equity in your home.
How Are Mortgage Rates Determined?
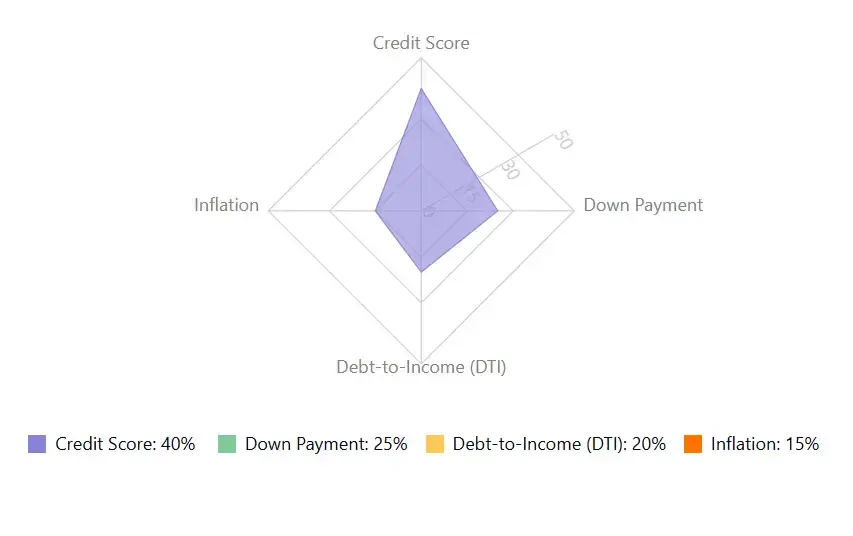
Home mortgage rate is determined based on the following factors:
Federal Funds Rate: While the federal funds rate does not have a direct relation to mortgage rates, both are correlated. Federal funds rate is the rate that banks charge each other when they lend money to each other. When the Federal Reserve increases this rate, the mortgage interest rates in the market usually increase too.
Inflation: When inflation rises, interest rates tend to increase due to increased demand by investors to increase bond yields, as the returns have less purchasing power.
Credit Score: Your credit score also affects the mortgage interest rate you are assigned. A higher credit score makes you a lesser risk, thus lenders tend to reduce your interest rate.
Down Payment: The higher your down payment, the lower your interest rate tends to be. This is because a higher down payment lowers your loan to value (LTV) ratio.
Debt to Income (DTI) Ratio: If your DTI is lower, which means your debt to income percentage is low, you can expect a better mortgage rate.
Some of the other factors that can influence mortgage interest rates include property type, occupancy, financing closing costs, market economic conditions, loan type, size, and term, government policies, and the geopolitical situation.
Types of Mortgage Rates
When you start your search for the best mortgage rate for your home purchase, you will come across many options. The most common ones are as follows:
Average Mortgage Rate: What to Expect
The average mortgage rate is constructed under the assumption that an equal number of consumers get mortgages every month, without any room for a refinance. For example, the average 30-year fixed mortgage interest rate that applies today is an average of the monthly marginal rates from the past 30 years. This process involves comparing the marginal rate with the average rate over time.
The average mortgage rate can fluctuate within a period of weeks or months. These fluctuations can especially be high during times of high volatility in the mortgage market.

30-Year Fixed Mortgage Rate vs. Adjustable Rate Mortgages
When it comes to mortgage rate comparison, you will want to differentiate between the 30-year fixed mortgage rate and the adjustable rate mortgages. The differences between the two are explained below:
30-Year Fixed Mortgage Rate
A 30-year fixed-rate mortgage is a housing loan having a repayment term of 30 years and a mortgage interest rate that stays the same over the term of the loan. The payment you make will be the same over the entire period.
So, if your first month payment is $1,300, your payment for the 12th month will also be $1,300. And so will be the payment for the 48th month. If the interest rate was 4% for the first year, it would still be 4% in years 10, 15, 20, and 29.
The fixed payment you make every month will be made up of an interest part and a principal part. You may also be required to pay a property tax and homeowners insurance premiums. Private mortgage insurance (PMI) premiums are generally required when the down payment is less than 20% of the house’s price.
Adjustable Rate Mortgage (ARM)
As the name suggests, an adjustable federal mortgage interest rate is variable. The interest rate that applies to the loan depends on the current interest rate trend. ARMs usually come with a fixed period for which the initial interest rate is kept constant. After this period ends, the interest rate will change at regular intervals. Some of the pros and cons of adjustable-rate mortgages are as follows:
Pros:
The monthly payments are usually lower initially
When the market interest rates fall, the rates on your ARM mortgage can also fall
If the interest rates fall over time, you can save more money compared to fixed-rate mortgages
Cons:
Your monthly payment can change frequently over the term of the loan
There is no way to tell whether the monthly payments will increase or decrease over time and by how much
ARMs went out of favor with many after the 2008 economic meltdown. Currently, there are stricter government regulations for the oversight of adjustable-rate mortgages.
Federal Mortgage Interest Rate and Its Impact on Borrowers
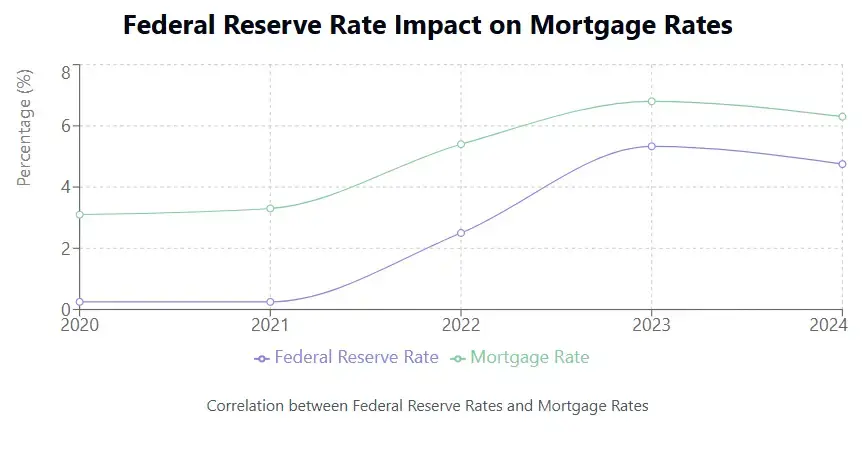
When studying federal mortgage interest rate and its impact on borrowers, it is important to know that the Federal Reserve is more interested in making an impact on short-term spending and less on long-term investments such as mortgages. This is why mortgages are often indexed to long-term indicators such as the 10-year Treasury bonds and not the federal funds rate.
However, as a borrower, you can find that whenever the Federal Reserve makes changes to its federal funds rate, there is an impact on the market mortgage rates. This happens because an increase in the federal funds rate means that lenders or banks will have to pay more to borrow money. There is a very high chance that they will transfer this increased cost to the consumer.
The federal mortgage interest rate also affects mortgage affordability. When federal funds rate increases and home prices too, there can be a decline in mortgage affordability.
Current Trends in Mortgage Rates
If you are looking for the best mortgage rate for yourself, it is important to know what the current trends are.
Current Mortgage Rate Overview
Recently, the average rate on a Freddie Mac-backed 30-year fixed mortgage came down to 6.87%. Previously, it was at an 8-month high figure of 7.04%. The current mortgage rate has been its lowest this year. The stability in the rate has been beneficial for potential homebuyers because the demand for homes is higher than it was last year at this time. This means that buyer activity an increase in the near future.
Mortgage Rate Predictions: What Experts Say
It is important to keep track of mortgage rate predictions from industry experts. The following forecasts can help you determine whether this is the right time to make your move, whether as a homebuyer or an investor.
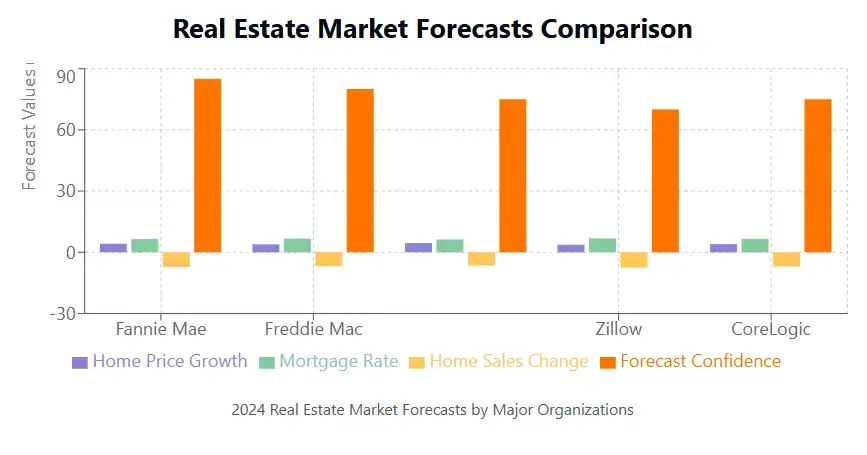
Fannie Mae: The Federal National Mortgage Association predicts the 30-year mortgage rates can drop to 6.50% in the near future. In 2026, the rates will reach 6.30%.
Freddie Mac: The Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation predicts that mortgage rates are likely to stay high in the near future and encourage more homebuyers to make their move because they are not going to wait for lower rates.
National Association of Realtors (NAR): According to NAR’s quarterly outlook, the 30-year mortgage interest rate will come down to 5.8% by the end of this year. The rates can then rise to 6.1% the next year.
Mortgage Bankers Association (MBA): The MBA has similar predictions as Fannie Mae’s. They see the mortgage rates to fall to 6.50% by the end of 2025 and 6.40% the next year.
Realtor.com: According to the popular real estate website, mortgage rates can come down to 6.20% by the end of this very year.
Reviewing Mortgage Rate History for Context
If you want to find the best mortgage rates, it is as important to look back at mortgage rate history as it is to look into the future. The following review of the history of mortgage rates can help you understand the real estate market better:
1970s: During the early 1970s, mortgage rates used to be around 7.25%. This was the time when Freddie Mac started tracking these rates. By the end of the 1970s, the rates had increased to 13% due to economic instability and high inflation.
1980s: The early 1980s saw inflation pushing the rates to 18%. Fortunately, by the end of the decade, the rates had fallen to an average of 9.75%.
1990s: Budget cuts and tax raises by the federal government saw the first budget surplus in a long time. A series of other factors too worked with this to bring down the mortgage interest rate to 7% by the end of the decade.
2000s: In the early 2000s, the interest rates averaged around 8%. By the end of the decade, the housing market crash brought about by the subprime mortgage meltdown pushed the rates to below 5%.
2010s: During the 2010s, the Federal Reserve was busy supporting economic recovery. In the early 2010s, the home mortgage rate fell to 3.31% and rose to just under 4% by the end of the decade.
2020 Onwards: The Covid-19 pandemic helped borrowers access the lowest mortgage interest rates in history. In early 2021, the rates fell to a staggering 2.65% before climbing to 7% recently on the back of high inflation.
How to Compare and Choose the Best Mortgage Rate?
Now that you understand mortgage interest rates, it is important to know how to compare and choose the best mortgage rate.
Mortgage Rate Comparison Tools
There are many online mortgage rate comparison tools that allow you to instantly compare different rates and terms from different lenders. There are many benefits of starting your homebuying process with the help of such a tool. This includes:
Save Time & Effort: These tools aggregate mortgage offers from different lenders and save you the time and effort of doing the research yourself.
Ease of Use: They can provide access to complicated mortgage data in a clear and concise way to help you compare your different options.
Helping Make Decisions: A mortgage rate comparison tool enables you to understand the differences between different loan options in terms of interest rates, fees, and terms. All this information helps you make informed decisions when choosing the right mortgage.
Factors Affecting the Best Mortgage Rate for You
There are many different factors that affect the interest rate that lenders offer you. It is important to understand these factors and their impact on your interest rate to make the right choice of mortgage. If you want the best mortgage rate, you should know about these factors that make a difference:
Credit Score: Your credit score is among the most important factors that affect the mortgage interest rate you are offered by lenders. The higher the credit score, the lower the interest rate tends to be.
Down Payment: The amount of money you can put down initially affects your interest rate. A larger down payment lowers your risk as a borrower and helps reduce your interest rate.
Loan to Value (LTV) Ratio: LTV ratio refers to the amount of loan availed against the property’s value. This ratio affects the loan’s risk and the higher it is, the higher the mortgage interest rate tends to be.
Term: The loan term or the period of repayment generally has a direct correlation to the interest rate. A shorter loan term tends to have a lower interest rate.
Economic factors, such as the federal funds rate, inflation, and the general economy also affect the home mortgage rate.
Home Mortgage Rate vs. Federal Mortgage Interest Rate: Key Differences
As already mentioned, the Federal Reserve does not directly set the mortgage interest rate. However, the federal funds rate eventually affects the interest rates. The federal funds rate impacts the 10-year Treasury note yield which affects how much consumers need to pay on the money they borrow.
The following points shed light on the relation between home mortgage and federal interest rates:
In May 2020, the federal fund rate was 0.05%. The 10-year Treasury yield touched 0.64% at the time. The 30-year fixed-rate mortgage’s average rate was 3.28% at the time.
More recently, the increase in inflation led the Federal Reserve to increase the federal funds rate. In August 2024, the 10-year Treasury yield stood at 3.99% while the 30-year fixed interest rate was 6.73%.
In January 2025, the federal funds rate increased to 4.33% and the 10-year Treasure rate rose to 4.53% and the 30-year fixed mortgage rate reached 6.96%.
Thus, the mortgage interest rate is generally directly proportional to the federal funds rate.
How to Secure a Low Mortgage Rate?
There are a number of steps that you can take to secure a low home mortgage rate.
How to Get the Best Mortgage Rate?
When you start shopping for the best mortgage rate, you will feel like the rates are determined by the market and lenders. However, you can take a number of steps to get better rates and save thousands, if not tens of thousands. This includes:
Improving your financial profile to increase your credit score
Putting down a larger down payment to reduce your loan to value (LTV) ratio
Paying discount points to bring down your mortgage interest rate
Exploring the advantages of first-time homebuyer programs
Shopping around with different lenders to negotiate better rates
Considering alternative mortgage types
How to Get a Lower Mortgage Rate Through Negotiation?
Whether you are a first-time homebuyer or seeking to refinance your existing mortgage, it is possible to negotiate and lower your mortgage interest rate. While negotiating, you will have to demonstrate how you are a creditworthy borrower. There is a good chance to get a better rate when you can show a lower quote from another lender.
It is recommended to follow these tips to negotiate better mortgage rates:
Shop around to get offers from multiple lenders
Find out which lender is ready to lower their interest rate offers
Use discount points to negotiate better rates
Improving Credit Scores to Reduce Mortgage Interest Rates
Traditional loans require borrowers to have at least a 620 credit score to qualify. If you want to improve your credit scores to get the best mortgage rate, it is recommended to follow these tips:
Check your credit score and history and raise disputes with credit rating bureaus for any discrepancies
Start paying all your bills on time
Bring down the balances on all your credit cards
Do not open new accounts
Conclusion
As a homebuyer, you will want to find the best mortgage rate. This requires exploring the different types of mortgage interest rates available in the market and understanding the impact of Federal Reserve decisions and economic factors on mortgage rates. It is also important to know that you can take several steps, such as improving your credit score, to get better rates.
FAQs:
What is the lowest home loan interest rate?
In January 2021, the home loan interest rates were at 2.65%, the lowest ever in history.
How can I get a 3% mortgage rate?
Currently, there is no special mortgage program that can offer a 3% interest rate.
Can banks offer lower mortgage rates?
Yes, banks can offer lower mortgage rates based on negotiation and your down payment amount.

